Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System in Iran - photos & map
![]() Author : Alirezaa | Date : Sunday 26 January 2025 12:51
Author : Alirezaa | Date : Sunday 26 January 2025 12:51

The Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System, nestled in Iran's Khuzestan province, stands as a testament to the ingenuity of ancient engineering. This marvel of pre-Islamic architecture, dating back to the 5th century BCE, showcases a sophisticated water management system developed to optimize the use of water for irrigation in the arid region. Recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage site, its significance extends beyond its technological achievements, highlighting its pivotal role in the evolution of Persian civilization and its enduring influence on urban water management practices worldwide. The system's global recognition underscores its historical and cultural importance, preserving a legacy of human creativity and interaction with the natural environment. The site has been referred to as "a masterpiece of creative genius" by UNESCO.
- Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System is open: Sun - Sat 8:00 AM - 7:00 PM.
- Entrance Fee: 2 USD - 1,000,000 Rial (100,000 Toman)
Visiting the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System
Visiting the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System offers a unique glimpse into ancient engineering and the rich history of Iran. Planning your visit carefully can enhance your experience, making it both educational and enjoyable.
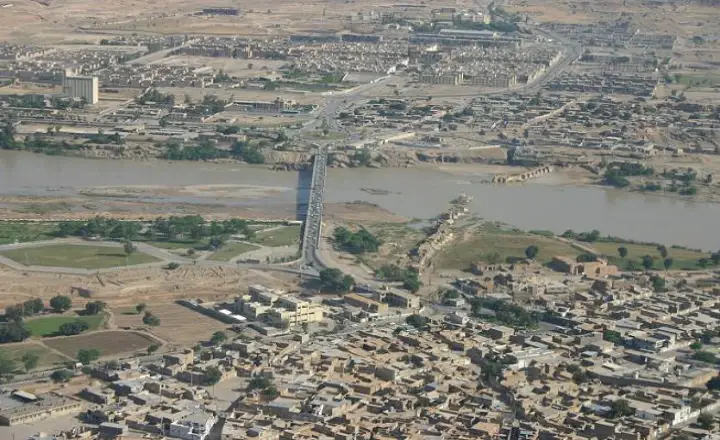

How to Get There: Transportation Options and Tips
By Air: The nearest major airport to Shushtar is Ahvaz International Airport. From Ahvaz, visitors can hire a taxi or use intercity buses to reach Shushtar, approximately a 90-minute drive away.
By Road: Shushtar is well-connected by road to major cities in Iran. Visitors can rent a car or use the extensive bus network. The journey offers a scenic route through the Iranian landscape, providing a glimpse into the country's diverse geography.
Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System - inscribed property UNESCO Official Map
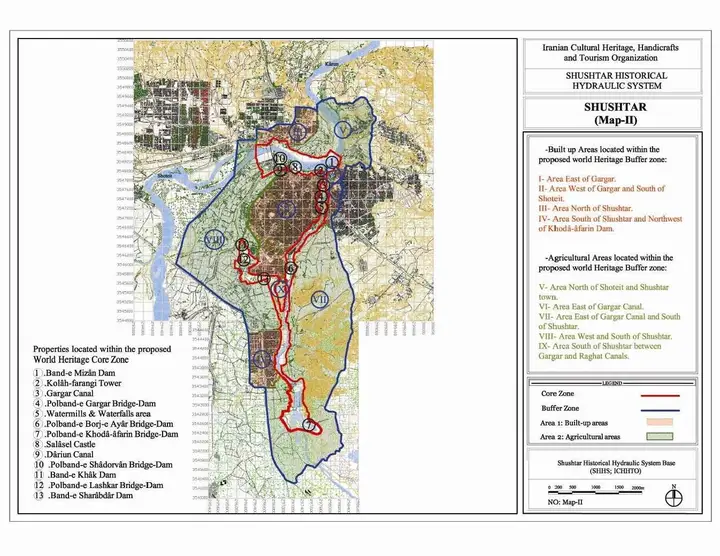
What to See and Do
Exploring the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System offers a fascinating journey through time, showcasing ancient engineering prowess and a deep connection with water and land. Here are the key highlights and activities to ensure a fulfilling visit.
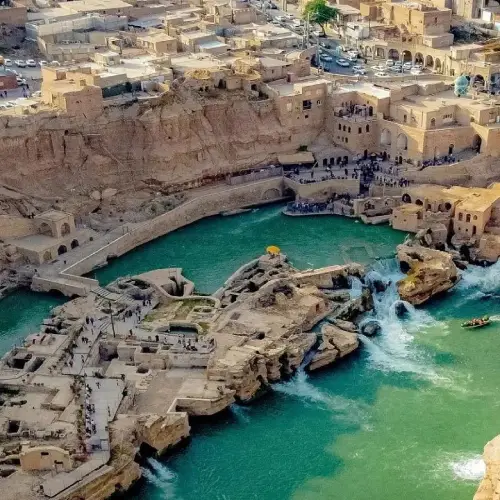

Key Attractions and Landmarks Within the System
Band-e Kaisar (Caesar's Dam): This ancient Roman-built bridge and dam is a standout feature, illustrating the blend of Persian and Roman engineering techniques. It played a crucial role in water management and is a must-see for its historical significance.
Water Mills and Waterfalls: The series of water mills, some of which are still partially operational, provide insight into ancient agricultural practices. The cascading waterfalls created by the mills offer breathtaking views and a serene atmosphere.
Salasel Castle: Overlooking the hydraulic system, Salasel Castle serves as the administrative center and offers panoramic views of the entire area. Its strategic location and architecture are impressive.
Gargar Tunnel: Engineered to divert water through the mountainous terrain, the Gargar tunnel is a testament to the ingenuity of ancient hydraulic engineering. Walking through or near this tunnel offers a unique perspective on the system's complexity.
Guided Tour Highlights: Must-See Parts of the Hydraulic System
The Dams and Tunnels: Understanding the design and function of the various dams and tunnels within the system is essential. Guided tours provide detailed explanations of how these elements work together to manage water flow.
Historical Context Presentation: Many tours offer insights into the system's construction, its significance in the Sassanian era, and its impact on the development of Shushtar and surrounding regions.
Operational Water Mills: Seeing the water mills in action, where possible, offer a live demonstration of ancient technology. Guides often explain the milling process and its importance in local agriculture and economy.
Activities in the Area: Boat Rides, Walking Tours, and Nearby Attractions
Boat Rides: Some operators offer boat tours along the canals, giving visitors a water-level view of the hydraulic system and its environment. It's a peaceful way to appreciate the engineering marvel and the natural beauty of the area.
Walking Tours: Walking tours through and around the hydraulic system allow for up-close exploration of its components. These tours can extend to the historical parts of Shushtar, offering insights into the city's rich history.
Nearby Attractions: Consider visiting the Shushtar Nooshijan Fire Temple, an ancient Zoroastrian temple, or the historical city of Susa, which is not far from Shushtar. Both offer additional perspectives on the region's ancient civilizations.
Visiting the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System is not just about witnessing an ancient engineering feat; it's an immersive experience of the culture, history, and technological advancements of ancient Persia. The combination of guided tours, leisure activities, and exploration of surrounding attractions makes for an enriching and memorable visit.
Architectural and Technical Details
The Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System is an exceptional example of ancient engineering, comprising an intricate network of dams, water mills, tunnels, canals, and buildings, all harmoniously integrated into a comprehensive water management and distribution system. This architectural ensemble was ingeniously designed to harness the power of the Karun River, Iran's most effusive watercourse, to support both agriculture and the needs of the city of Shushtar.
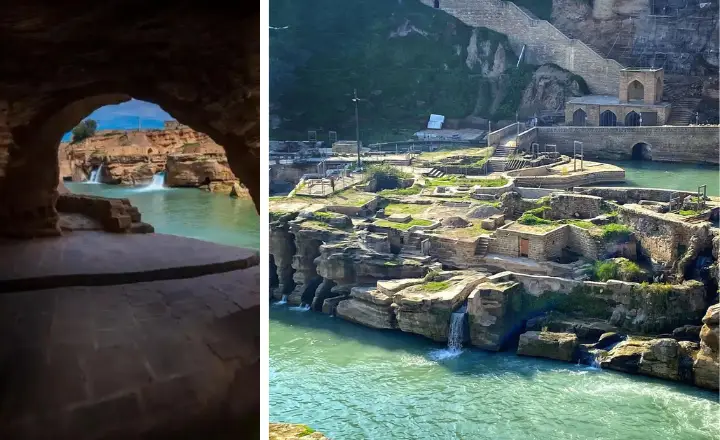

Components:
- Dams were constructed to divert river water into the system. The most notable, the Band-e Kaisar (Caesar's dam), believed to have been built by Roman prisoners of war, also served as a bridge.
- Water Mills form a significant part of the system, with structures built to leverage the flow of water to grind grain. This was a remarkable feat of engineering that predated modern industrial mills.
- Tunnels were carved through the rock to direct water flow across various parts of the system, ensuring a steady supply to the city and its agricultural fields.
- Canals were skillfully designed to distribute water throughout the area, supporting both urban water supply and irrigation for farming.
- Buildings associated with the system include water regulation structures and mill houses, which facilitated maintenance and operation.
Engineering Marvels:
The system's design demonstrates an advanced understanding of hydraulic engineering principles. Engineers of the time mastered techniques to manage seasonal floodwaters, channel water through tunnels and canals across varied terrain, and utilize gravitational force to operate mills. This level of sophistication in water management and mechanical engineering was unparalleled for its time.
Role in Irrigation and Urban Planning:
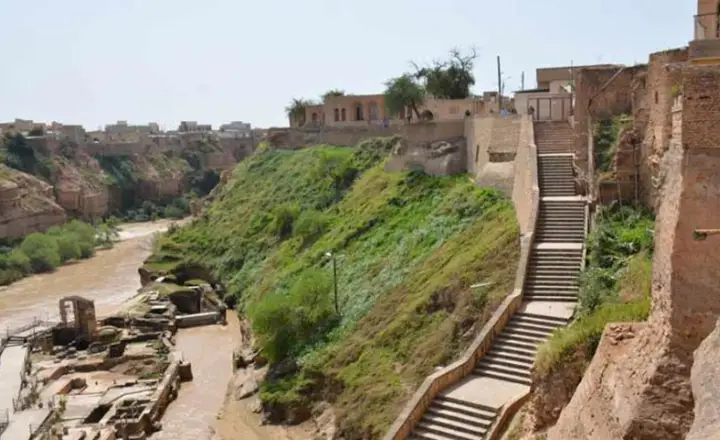

The Shushtar system was pivotal in transforming the surrounding desert landscape into fertile agricultural land, enabling sustained urban settlement in an otherwise inhospitable region. It facilitated year-round farming, significantly boosting the local economy and allowing for population growth and urban development. The system's integration into the city's fabric exemplifies early sustainable urban planning, balancing natural resource management with the needs of a thriving urban center.
In summary, the architectural and technical achievements of the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System not only underscore the ingenuity of ancient Persian engineers but also highlight their foresight in urban planning and environmental sustainability. This historic system remains a symbol of human ingenuity in harmonizing the built environment with the natural world.
Technological innovation and its impact on the local community and agriculture
The Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System represents a pinnacle of ancient technological innovation, profoundly influencing the local community and agricultural practices in its vicinity. This intricate network of dams, canals, water mills, and tunnels not only showcases the advanced engineering skills of ancient Persians but also reflects a deep understanding of sustainable water management. Its construction catalyzed economic prosperity by bolstering local industries, especially grain milling, and facilitated urban development, transforming Shushtar into a flourishing city. The system fostered a cooperative social structure, with communal efforts centered around its maintenance and operation. Agriculturally, it revolutionized farming practices by converting arid lands into fertile fields, enabling year-round cultivation and increasing food security. The introduction of such sustainable irrigation practices minimized water waste, showcasing an early recognition of the importance of conserving natural resources. Thus, the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System not only served as a backbone for economic and urban growth but also as a testament to ancient wisdom in harmonizing technological advancement with environmental sustainability, leaving a lasting legacy on both the local community and the landscape it nurtured.
Read More: Kerman travel Guide - Tehran Travel Guide - Shiraz Travel Guide - Tabriz Travel Guide - Qeshm Travel Guide - Kashan Travel Guide - Hamadan Travel Guide - Kermanshah Travel Guide
Last Word
Visiting the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System offers an unparalleled opportunity to witness firsthand the ingenuity of ancient engineering and its lasting impact on civilization. This UNESCO World Heritage site not only highlights the sophisticated water management techniques of the past but also serves as a vivid reminder of humanity's ability to adapt and thrive in challenging environments. Exploring the system and its surroundings allows visitors to step back in time and appreciate the intricate relationship between humans and nature. For those looking to delve deeper into the history and significance of this ancient marvel, a wealth of resources, including scholarly articles, documentaries, and books, are available. Engaging with these materials can enrich one's understanding and appreciation of the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System, encouraging a deeper exploration of the ancient world's technological achievements.






